Under article 69 of the Code, the mother of a minor may initiate the deprivation of the father ' s parental rights for failure to pay maintenance, and it is important to know the grounds, collect evidence and use the step-by-step instruction on deprivation through the courts.
Could the father ' s parental rights be revoked for non-payment of maintenance?
The possibility of depriving a child of his or her parental rights is specified in article 69 of the Code of Criminal Procedure. The procedure is permitted in the case of a parent who has deliberately evaded the payment of maintenance provided for by an executive record (IL) or a court order.
Reasons for depriving the father of his parental rights
The term "wrong evasion" should be understood to mean non-payment of maintenance for more than four months without good reason solely because of the fault of the payer; the main signs of "grudging" are contained in the FSP letter of 19 June 2012 No. 01-16, which should be used by the bailiffs to determine the extent of the guilt of the person under obligation.
This list includes:
- Deliberate concealment of real profits;
- The absence of a response to the warning of possible prosecution of the CoA of the Russian Federation;
- Concealment of property liable to recovery;
- Change of place of employment or residence without notice to the bailiff;
- :: Providing information that is known to be unreliable about earnings and property.
These factors can be applied either separately or in an integrated manner; the main condition for recognition of maintenance obligation by a hard-core non-payer is a delay in payment for more than four months.
Administrative measures are the softest and are used as a warning; if the debtor has not responded and has continued to accumulate debts, the next step may be liability under article 157 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation.
It's important that you don't have to wait for criminal responsibility if you're gonna be deprived of your parent's rights: it's enough to build up a debt for four months.
This is also the view of the Russian Federation ' s Plenum, which stated in its Decision No. 44 of 14.11.2017 that the length of the delay must be taken into account and that the reason for the non-payment is also taken into account. If it is established that the person under obligation has not paid the money due to illness or disability, he may be relieved of the debt in part or in whole (article 114 of the Russian Federation).
Consequences of deprivation of parental rights
The main consequence for the deprived person is the lack of rights to the child; according to article 63 of the Code of Criminal Procedure, rights refer to the possibility of bringing up, educating and treating a minor at his or her discretion, but on the basis of his or her opinion.
With the loss of rights, the parent will not be able to see the child or communicate by telephone, and the following consequences are also relevant:
- Failure to recover maintenance when the child reaches the age of majority if the person deprived of his or her liberty is declared incapable of work;
- All envisaged and formal social benefits are abolished;
- There will be no need for permission to take legal action or to leave the country;
- may leave property to a minor and evict a person deprived of his/her liberty if he/she lives in the same room under a social employment contract;
- A child ' s property may not be claimed in the event of his or her death.
The consequences for the child are that they cannot communicate with the father or mother and that they retain the right to maintenance and inheritance upon the death of the deprived parent.
The most positive is for the second parent:
- The possibility of leaving the Russian Federation or changing the country without the written permission of another parent;
- Prohibition of meetings with persons deprived of their liberty;
- The adoption of a minor by a new spouse (s) without the consent of the deprived person is permitted.
The main reason why mothers seek to deprive former spouses of parental rights is the desire to receive child support without subsequent recovery by the payer when the child or daughter reaches the age of majority.
Even if a child is placed in a state institution, you'll still have to pay alimony.
Maintenance debts after deprivation of parental rights
The deprivation shall not affect the amount and calculation of maintenance, and they shall be paid as maintenance until the child reaches the age of majority; the exception shall be adoption, but it shall not be permitted until six months after the date on which the decision of the court becomes enforceable.
If the debt has already accumulated, it will have to be paid after the withdrawal, which is not a basis for debt relief.
Procedure for the deprivation of parental rights for non-payment of maintenance
The deprivation procedure can be carried out in one of two ways: the first is the simplest and involves a minimum of effort and time:
- Information on debts is requested from the bailiff.
- An application shall be submitted to the guardianship authority; the court may not hear an application for withdrawal without its representatives and the Public Prosecutor ' s Office; the latter is notified of the custody itself.
- The characteristics are collected. You can ask for a questionnaire on the debtor from the workplace. It is good if the employer characterizes the person being deprived as negative: this will be an advantage for the plaintiff. It will be an important characteristic from the child ' s place of study, indicating that the parent is not in contact with him. It will also be necessary to have this document from the employer and from the plaintiff. It must indicate the reliability, sufficient income and optimal socialization of the parent.
- An application is submitted to the court, which, after having considered it in five days, the judge shall set the date of the first hearing.
- The parties are present at the hearing and present arguments and evidence, on the basis of which an objective decision is taken, which becomes enforceable after one month, after which an extract from it shall be sent by the court to the registry office.
The second option of deprivation involves prior criminal prosecution of the debtor, pursuant to article 50 of FL 229, the applicant has the right to apply for it by filing a written statement with the bailiff.
- An application for the engagement of a debtor under article 157 of the Criminal Code is sent to the FSP officer in charge of the execution proceedings.
- The bailiff examines the application, determines whether there are grounds, sends a maintenance notice to the debtor requesting payment of the debt and an indication of the possible consequences in the case of non-payment.
- If the money is not received within the prescribed time limit, the bailiff prepares the case file for transmission to the person conducting the initial inquiry.
- The person conducting the initial inquiry shall, after a number of procedural actions, send the documents to the Public Prosecutor ' s Office.
- The case is brought before a court, resulting in the sentencing and adoption of measures under article 157 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation.
When the debtor carries out the prescribed sentence, the offender goes on to take the next step of disenfranchisement, in which case it will be easier to obtain a favourable decision, i.e. the existence of the sentence already indicates a vicious character. If you go along the first path, the court will have to determine the degree of guilt of the maintenance obligation itself.
It's also important to know: How do you withdraw the maintenance paper?
Jurisdiction
Cases of disenfranchisement within the jurisdiction of the district courts: documents should be filed with the judicial authority of the defendant's place of residence; if it is not known, the location of his property.
Statement of claim
The following data will be required for the preparation of the claim:
- Name of judicial authority;
- FIO, registration address, applicant ' s passport;
- FIO, date of birth of the defendant;
- FIO, certificate and date of birth of the child on which alimony was collected;
- The IL number on the basis of which the alimony was to be paid;
- The date of the last payment for the maintenance of the minor;
- A description of the circumstances and signs of malicious evasion;
- Total debt;
- The period in which the debt accumulated;
- An inventory of the attached documentation;
- Date of writing and signature.
Catherine Derjavina
Assistance in drafting claims and other legal documents
The application shall be filed in two copies. One shall remain in court: a copy shall be removed and sent to the defendant, the original shall be attached to the case file. The other shall bear the registration mark, which shall be returned to the plaintiff.
List of documents attached to the suit
If applied to the court, it will be necessary to:
- Passport;
- Child birth certificate;
- A receipt for the payment of the public service;
- A court order for payment or an IL;
- A decision on the calculation of arrears.
Collection of evidence
The evidence shall be:
- Reports from the SPF;
- Bank statements to which the money should have gone;
- The characteristics and testimony are important.
The latter are needed to confirm that the father has not participated in the child ' s life.
The size of the State and the time frame for the consideration of the case
According to article 333.19, paragraph 3, of the Code of Criminal Procedure, 300 roubles must be paid before a claim for deprivation of liberty is brought, and the State is not paid only in the event of the recovery of maintenance.
The maximum duration of the proceedings is 2 months from the date of the complainant ' s application until the judgement is delivered; the time limit may be extended by the court when applications from the parties are filed for reasonable reasons, but this is very rare.
Judicial practice
In cases of deprivation of parental rights, judicial practice was mixed: after examining documents and evidence, the court had to take a reasoned decision, and it was not always in favour of the plaintiffs.
Loss of parental rights of the father, mother for non-payment of maintenance
The Main "Appliances "Loss of parental rights of the father, mother for non-payment of maintenance
284 views
Wicked non-payment of maintenance can lead to serious consequences.
The amount of the debt begins with a penalty, followed by additional fines, seizure of property, suspension of driver ' s license, prohibition of cross-border movement, forced labour, and so on, eventually leading to deprivation of parental rights and imprisonment.
Can parental rights, paternity for non-payment of maintenance be revoked
Article 69, paragraph 1, of the Code of Criminal Procedure states that parents may be deprived of their parental rights if their duties with respect to their children are deliberately avoided; one such fundamental duty is to support the child; in particular, the payment of maintenance; if a person fails to pay the sums due for a long period, he or she will be deprived of his or her rights with respect to the child.
It will be absolutely irrelevant why no payment has been made: malicious intent and deliberate evasion of duties or a mere lack of funds; this is related to article 80 of the UK (para. 1). It states that parents are obliged to support a child.
There is no reservation, however, that this factor is somehow linked to wages in general or to any existing/non-existent income in particular.
Thus, even if parents do not earn anything at all and do not have the means to live for themselves, they are still obliged to look for them to support the child; this is true of both the maintenance situation and the relatively healthy family.
Since it is not possible to deprive a father or mother without good reason, first it must be proved that there are reasons for doing so:
- The parent is not involved in the child's life.
- The parent doesn't pay alimony.
The first factor is often difficult to prove, except that the child ' s father or mother did not participate in his or her life from the moment he or she was born and are not going to change anything. The second factor is used much more frequently, but, importantly, the desired effect is most likely to be achieved if both factors are present.
Example: If the payer does not have the money to pay maintenance, but he tries to compensate it by communicating with the child, gifts, individual activities for his development or any other means, it will be difficult to deprive such a person of his parental rights, and a very different matter if he does not simply pay, but does not want to see his own child. In the latter case, it is more likely that such a non-payer will not even resist being deprived of his rights.
The deprivation of parental rights can be done by means of an application to a court, and the procedure usually includes the determination of the future procedure for the payment of child support, and there are two main methods by which this can be done:
- To apply directly to the court and to demand that the parental rights of the non-payer be revoked.
- First, to initiate criminal proceedings concerning gross non-payment, and then, when the maintenance worker is brought to justice, to apply to the courts.
Regardless of the path chosen, the general course of action with the deprivation of rights will be approximately the same.
Mode of action
- To collect documents and evidence that the spouse has evaded his or her duties; this includes criminal proceedings.
- To prepare a statement of claim along the lines set out below.
- Send an application to court in person or by post.
- Wait for the date of the meeting.
- Get your hands on the court's decision.
- Wait until it enters into force and adhere strictly to all paragraphs of the document.
A defendant who disagrees with the decision may file a counter-claim, an appeal or a separate application for reinstatement.
Example:The non-payer may disagree with the court ' s decision and file an application for reinstatement.
The reason given is that a person actively interacts with a child, influences his or her development, looks after him or her when required, conducts individual activities and so on.
If, in such an application, the payer also writes that he undertakes to pay all the maintenance debts that have been incurred over a period of time and does not permit their subsequent appearance, the court may agree with him.
To download a sample of the application for deprivation of parental rights
Jurisdiction to carry documents
The application should be submitted to the Magistrate ' s Court of Habitat/Registration/Residential, which would significantly expedite the procedure, thus producing the necessary results much earlier.
It should be borne in mind that, at the outset, the matter was dealt with only by the Magistrate ' s Court, and only if it had rendered the wrong decision to the plaintiff could it be tried before a higher authority.
When such a matter is brought before a court, the plaintiff does not defend his or her rights but the rights of the child; as a result, the government is not paid; in some cases, the case may be considered to be non-pecuniary, which means payment of a duty of 300 roubles; in any case, it is not the plaintiff who pays the money, but the defendant who pays it.
What documents are needed to remove parental rights: list, list
List of documents to be provided to the court:
- The applicant ' s passport.
- The baby's birth certificate.
- A certificate from a kindergarten, school, or other similar institution about who brings and takes the child, as well as who works with him, comes to the parents' meetings and so on.
- Testimony as to whether or not the maintenance worker is involved in the child ' s life.
- The characteristics of the place of work/student of the payer.
- Certificate/sentence of maintenance received or not received.
The package is not complete; it may vary depending on the situation.
Once one parent is deprived of his or her rights to the child, the other receives the following opportunities:
- To leave the country without the need to seek permission from a second parent.
- Change the child ' s data (in particular the FIO).
- Stop the other side from trying to interact with the baby somehow.
- Allow adoption of a child by a third person (for example, a stepfather).
The deprivation of rights also implies the automatic deprivation of the child ' s duties vis-à-vis his/her second parent.
- To keep your mother or father in old age.
- To defend his rights or interests.
- Hand over part of the inheritance as heir to Phase One.
Characteristics of deprivation of parental rights of mother, father (model)
One of the important documents to which the court pays particular attention is the description of the maintenance worker, which is often written at the place of work, but can also be written by any other official who in one way or another refers to the non-payer.
This document is required to include:
- Name.
- The person to whom the characterization is written.
- Description of the characteristics of the person.
- Information from the passport.
- Signature and date.
The more negative the profile, the more likely a person is to be deprived of parental rights.
Example: Ivan Pavlović does not pay child support and seeks to communicate with him, and immediately after his birth he divorced his wife and never appeared in her life.
At work, he is known for his sloppy nature, often making gross mistakes that result in losses to the enterprise, and may also appear in the workplace in a drunken state, a characteristic that is likely to contribute to the deprivation of parental rights.
Cedor Petrovich, however, does not pay alimony because of a small salary, constantly helps his ex-family, communicates with the child and educates him.
At work, he has a well-deserved status as a drummer and frontman, participates actively in the life of the collective, helps new recruits, does not drink or smoke, and such a characterization will be very difficult to obtain because the court is reluctant to take such measures.
Judicial practice
Example No. 1:: A case involving the deprivation of parental rights by the mother of the child is pending before the court; the child is currently living with his grandmother, who also manages, provides for and develops the child ' s parental rights.
After the baby's birth, the mother left the baby with her grandmother and, on the basis of the characteristics obtained at the school, from the first grade, the baby was always followed by her grandmother, and the mother was never seen there.
It should also be noted that the mother does not contribute money to the child ' s maintenance, and the child has confirmed that the mother sees her very rarely and rather by accident than by accident, although no one prevents her from doing so.
18 and 3), as well as articles 73, 63 and 65 of the Family Code of the Russian Federation, decide to grant the deprivation of parental rights.
Example No. 2The mother filed a lawsuit against the father for the deprivation of his parental rights on the grounds that he did not provide her with child support; as evidence, a statement was provided from an account stating that there were no transfers from the man; the defendant in turn provided other evidence: receipts stating that the money had been handed over in cash, checks for the purchase of children ' s toys, video recordings of the child ' s activities, and receipts from various developing sections for the child, which were also paid by the father; the description of the work of the maintenance worker as a generally positive person; the court rejected the claim; it should be noted that, in such a situation, the mother could be held criminally liable under article 307 of the Criminal Code for making known false statements.
The deprivation of parental rights with maintenance in 2023 is a normal process; if a father or mother gives up a child, it does not mean that they do not have to support and support it.
Thus, deprivation of rights does not imply deprivation of duty, which means that the father who is deprived of maintenance is still obliged to contribute to the child ' s maintenance.
It is only when the child reaches the age of majority or when he or she has another person ready to assume such responsibilities (e.g. stepfather).
We need a lawyer.
The process of deprivation of parental rights is a complex process that takes into account the great variety of features and nuances. Only an experienced lawyer can handle it. Our specialists can help solve the basic issues for free consultation, but the speedy resolution of the case requires the full support of both the non-payer and the court.
If you want to solve your problem, then...:
- Please describe your situation to the lawyer on the online chat room;
- Write the question in the form below;
- Call +7.499)369-98-20 - Moscow and Moscow Region
- Call +7.812)926-06-15 - St. Petersburg and Region
Claims for deprivation of parental rights and recovery of maintenance – how to write where to file, grounds for deprivation of parental rights
According to the UK, in particular the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation and other legislation, if the parent fails to fulfil his or her duties towards the child, harms him or her, endangers him or her, he or she may be deprived of his or her parental rights, but this does not relieve him or her of the need to support his or her child financially, i.e. to pay maintenance properly.
The situation would seem somewhat paradoxical, but in judicial practice it is not uncommon.
The classic case is that the father does not take part in the child ' s upbringing, has an immoral lifestyle, nor does he have a parent at all.
In such a case, the mother has the right to deprive him of his parental rights through a court of law, and in addition to recovering alimony from him, he is still a biological parent, a fact not even rebuttable by the court.
In such a case, the father does not have the right to raise, demand to see the child and have any influence on him or her at all, but is obliged to fulfil his or her financial obligations.
Grounds for deprivation of parental rights
What's important is that even if the defendant, in this case an unfriendly parent, does not appear in court, it will not have a positive effect on him – the judge will decide in absentia, and without his participation.
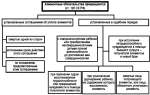
The grounds for depriving parents of their parental rights are as follows:
- Failure to perform parental duties.
- Drug or alcohol addiction.
- Child abuse, abandonment – these two paragraphs already speak of criminal responsibility.
- A threat to the life and health of the child.
- The refusal to take the child out of the institution is a maternity home, a hospital, and so on.
- Failure to pay maintenance.
It is the last item that we will consider further in detail.
Can rights for non-payment of maintenance be revoked?
Let's take a look at this from a non-legal perspective: a parent has to take care of his child – raising, protecting, sheltering and feeding, education, and so on – it's just a small part of his responsibilities, and it doesn't matter whether he lives with him or not.
If a parent doesn't pay alimony, he says, "I don't want to support my child, I don't have money for it." Can he call a parent with that attitude?
It is also the view of the UK that failure to pay alimony for more than six months without good reason constitutes a systematic violation of its parental duties and constitutes a serious ground for disenfranchisement of rights.
According to article 78 of the UK, such matters are decided by the courts and the guardianship and guardianship authority must be present at the hearing.
An application for withdrawal of parental rights for non-payment of maintenance may also be submitted under article 157 of the Criminal Code.
To be clear, this article deals with the penalty for malicious evasion of maintenance payments for more than four months without a valid reason.
The UK of the Russian Federation states that it is possible to deprive parents of their parental rights for a criminal offence against a child, so that in this case the parents will also be involved for a criminal offence.
Where should I go?
A claim for deprivation of parental rights and recovery of maintenance shall be submitted to the Magistrate ' s Court of District or City of the parent ' s and child ' s place of residence.
If the defendant ' s whereabouts are unknown, he may be reported to the executive.
What documents need to be prepared?
The basic documentation package consists of the following:
- The plaintiff's civil passport.
- The birth certificate.
- A marriage certificate, if you have one.
- A divorce certificate, if any.
- The documents on the basis of which the alimony must be listed are an agreement, an executive note.
- Family profile.
- A residence certificate that will confirm the child ' s residence with the claimant ' s parent.
- Documents that confirm that there is no deposit of maintenance, such as a bank statement.
- Evidence that the parent is failing to perform his parental duties.
You'd better consult a lawyer first, he'll tell you exactly what documents are needed in your situation, and he'll make a proper case. You can get free advice from our lawyers online on the website.
Model claim
The model of the claim for the deprivation of parental rights of the father or mother is not standardized, but must necessarily conform to procedural rules.
- Name of judicial authority, address.
- Judge's FIO.
- FIO, address of the plaintiff's residence.
- FIO, if known, the address of the defendant ' s residence. If no such information is available, indicate "the place of residence is not really known".
- Reasons for filing a complaint: failure to perform parental duties, failure to pay maintenance (require from what period, if any, measures have been taken to resolve the matter in pre-trial proceedings).
- The requirement to satisfy claims on the basis of the evidence listed, as well as the relevant articles of the law.
- List of attached documents.
- Date and signature with decryption.
A claim for deprivation of parental rights for non-payment of maintenance shall be filed in four copies: the defendant, the judge, the guardianship and guardianship authority, and the plaintiff.
With regard to the attached documents: copies may be attached, but the originals must be accompanied at the trial.
Nuances and jurisprudence
In the case of deprivation of parental rights for non-payment of maintenance, the court will necessarily consider the performance of parental duties as a whole, and it is clear that immoral behaviour of the parent, ill-treatment of the child, abandonment of the child and the like will be an aggravating circumstance.
The views of the child in such situations are, of course, taken into account first and foremost: from the age of 10, he or she can report this to the court on his or her own; before that age, the child must be interviewed by a child psychologist and give his or her expert opinion, which the court may also take into account.
As for guardianship and guardianship authorities, they had to give their "conviction" on the situation, the court could take recommendations into account but did not have to take them into account.
Let's take stock.
The claim for the deprivation of parental rights and the recovery of maintenance shall be submitted to the global city or district court of the parent ' s and child ' s place of residence, which shall not be dismissed by the State, and shall take into account all factors in the parent ' s and child ' s relationship, since the deprivation of parental rights shall be a measure of last resort.
Loss of parental rights of the father or mother
Principal maintenance / deprivation of parental rights of the father or mother
Previews 2978
The number of children left without parental care is increasing every year.
Although family law provides that fathers and mothers who are deprived of parental rights are not relieved of parental responsibilities (in particular the obligation to provide for their children), in practice this is much more difficult to obtain from the parents the payment of child maintenance money; in this article we will examine the procedure for the recovery of maintenance after the deprivation of parental rights.
Reasons and reasons for deprivation of parental rights
In order to initiate the process of deprivation of parental rights, there must be strong grounds. The law provides a list of the reasons why this is possible:
- The parent avoids the payment of maintenance and fails to fulfil his obligation to provide for the child (as evidenced by the certificate of maintenance arrears);
- The parent refuses to remove his newborn child from the health facility;
- The parent is violent (physical, sexual, psychological) towards the child;
- The parent is abusing alcohol or drugs (confirmed by a certificate from the drug clinic);
- The parent commits an offence against the child or another member of the family (as confirmed by the court ' s judgement);
- A parent abuses his or her rights, for example by unduly preventing a child from communicating with another parent or family member, by prohibiting the child from travelling abroad, by initiating a transfer from school to school or by prohibiting him or her from going to an educational institution altogether.
Is it possible to take away the parental rights of someone who pays alimony?
As mentioned above, one of the reasons for the deprivation of parental rights may be non-payment of maintenance, but this does not mean that a parent who fulfils his maintenance obligations in good faith may not be deprived of parental rights.
Articles 63-65 of the Family Code list parental responsibilities, which include not only the obligation to provide for the child but also to raise him or her, to care for his or her health, to promote his or her education and full development.
For example, in addition to unemployment and non-payment of maintenance, a parent ' s negative influence on the child, prohibition of school attendance, lack of necessary care for the child, failure to comply with a doctor ' s instructions in the event of a child ' s illness and so on may be the reason for the deprivation of rights.
Application to court for deprivation of parental rights
We will consider below how to implement the legal procedure for depriving the father or mother of parental rights.
Who can sue for the deprivation of parental rights?
A second parent, as well as the child ' s guardian or guardian, may initiate the process of deprivation of parental rights, but they are not the only ones.
Officials (prosecutor) and public or municipal authorities (the guardianship and guardianship authority, the administration of the orphanage or the children's home) also have the right to claim the deprivation of parental rights.
Other persons (e.g. relatives, teachers or educators of educational institutions) are not entitled to bring an action before a court, but they are entitled to apply to competent officials or authorities for such an initiative.
List of documents submitted to the court
- Passport;
- The marriage certificate (if it is concluded between the child ' s parents) or the dissolution of the marriage (if it is dissolved);
- The birth certificate of the child;
- An extract from the home book on the registration of the plaintiff and the defendant by place of residence;
- Act on the inspection of housing conditions, in the child ' s place of residence;
- The characteristics of the plaintiff and defendant workers, issued at the place of employment of each of them;
- Characteristics of a child from a school or pre-school educational institution;
- Parental income certificates (2-NFFL) and evidence of additional sources of income (e.g. lease, contract);
- Certificates from the bailiff ' s office on the existence of maintenance debts;
- Certificates from a medical institution;
- Other documents confirming the failure of the parent to perform his duties or to deviate from the generally accepted standards.
This is only an approximate list of documents that can be attached to the claim; it can be supplemented or amended according to the particular circumstances.
For example, if the parent was violent, beaten his children, the testimony of witnesses as well as the medical reports of the child ' s examination, administrative records could be used as evidence.
The testimony of a child or of a witness may be the testimony of a parent who has attempted to harm the child's sexual integrity; and if there is a judgement in this case, he shall be admitted to the case as evidence.
If the parent has committed a crime against his or her family members (against the second spouse or child), a judicial sentence must be handed down that has entered into force.
If the parent suffers from chronic alcoholism or drug addiction, this must be confirmed by a certificate from a medical institution (dispersor), and if the parent is already limited in capacity, a court decision must be attached.
The more convincing, uncontroversial evidence will be produced, the faster and more concise the trial will be.
Application for withdrawal of parental rights of the father or mother
In addition to the package, a correct statement of claim is filed with the court.
The statement of claim consists of three main parts: a "scape", a description of the circumstances and the motivation of the claims, the formulation of the claims, and a list of annexes. Consider each element of the statement of claim in more detail.
The first element, the so-called "scape", should contain information on the parties to the deprivation of parental rights proceedings: the courts, the plaintiff, the defendant, the third of the persons, as follows:
- Name and address of the court where the claim will be heard;
- Data on the plaintiff and defendant — F.I.O., date of birth, place of registration and residence, contacts;
- Name and addresses of third parties to the proceedings - the guardianship and guardianship authority, the prosecutor;
- Note on the amount of State duty, payment or exemption from payment.
Next is the title of the document, "A declaration of deprivation of parental rights".
The second element of the statement of claim is referred to as "description and motivational." The circumstances of the case are summarized briefly, accurate and informative. It should be indicated when and where the marriage was concluded, the names of the children born in wedlock, with the indication of F.I.O. and the date of birth. If the marriage has been dissolved, the date and cause of the divorce must be indicated.
A description of the grounds for depriving the father or mother of parental rights should then be given of the evidence supporting these grounds; it is not necessary to list the legal provisions that give the right to apply to the court for the deprivation of parental rights.
The final, third element of the statement of claim is "reservative", where claims must be formulated, such as deprivation of parental rights, recovery of maintenance from a parent deprived of rights.
The main part of the statement of claim is followed by a list of documents attached to it.
The statement of claim shall conclude with the claimant ' s signature, specifying the date of writing.
How do you file a lawsuit?
So, you've managed to write a statement of claim, you've prepared a stack of documents. What do you want to do next? Go to court - file a lawsuit.
We're gonna give it to you downstairs.A few useful clues as to how to file a claim:
- Applications are not accepted in court 24 hours a day, there are certain reception days and watches, usually on a public spot in the courthouse or on a website.
- An application and a package of documents should be prepared in as many copies as the number of parties involved in the trial; generally, it is the court, the plaintiff and the defendant, the interested persons – the prosecutor and the SRB – that requires four sets of documents to go to court, which will be sent to the court office after the case has been accepted; and better yet, with five, an additional package of documents with an indication of acceptance will be kept.
- The documents that are filed with the statement of claim must be in copies, but they must be accompanied by the originals so that the court can verify the accuracy of the copies and assure them of your presence.
- The State duty must be paid before a claim can be filed, and the bill of payment must also be added to the claim.
State Ministry in 2023
Since the beginning of 2015, the Tax Code has been amended with regard to the amount of the State duty.300 rubles(article 333.19 of the Code of Criminal Procedure).
If other claims, such as alimony, are made at the same time as the deprivation of parental rights, the amount of the State duty may be changed in accordance with the cost of the claim.
Where to go?
A ready application, together with a package of necessary documents, is filed with the district (city) court at the defendant's place of residence, the parent who must be deprived of parental rights.
Procedure and procedure for the deprivation of parental rights
As can be seen from the foregoing, the only authority competent to deprive parents of their parental rights is the court, and on the basis of the application, proceedings are instituted in which the parents, the child(s), the procurator, the guardianship and guardianship authorities are involved.
The judicial process of deprivation of parental rights is lengthy and complex; the court carefully analyses the circumstances, examines the psychological and social profile of the parents and children, checks the data contained in the claim and ascertains the credibility of the evidence provided.
The court (as well as the prosecutor and the guardianship and guardianship authority) has the right to request from the parents the necessary documents directly relevant to the case (certificates of birth, marriage and divorce, certificates - medical, income, family composition, etc.) The court is guided not only by the evidence provided by the plaintiff but also by the conclusions of the prosecutor, the guardianship and guardianship authority.
In deciding on the deprivation of parental rights, the court decides on other related matters: custody of the child, determination of the child ' s place of residence, recovery of maintenance from the disenfranchisement of the parent; if the applicant has a position in this regard, it should be presented in the application or in the form of an application to the court.
Consequences of deprivation of parental rights
All the consequences that arise after the deprivation of parental rights are laid down in article 71 of the Family Code.
First of all, the parent is deprived of all rights based on blood relations between him and the child, and no longer has the right to see and communicate with the child, to raise him, to defend his interests, to be his legal representative.
Such a parent loses the right to maintenance from the child in the event of incapacity and hardship and the right to legal inheritance after the child ' s death.
A father (or mother) who has been deprived of parental rights loses all State benefits related to the presence of children.
All of the above consequences of the deprivation of parental authority are a form of punishment for fathers and mothers who neglected their duties.
However, this penalty applies only to parents and should not have a negative impact on children; children retain the right to maintenance from their parents, to pay additional expenses (education, treatment), to use the parent ' s home and to inherit legally after his death.
In order to ensure the rights of children, the legislature provided for the possibility for the father (or mother) who had been deprived of parental rights to be rehabilitated and restored; until the parent restored them in accordance with the procedure established by law, the consequences listed above would remain.
Maintenance payments after deprivation of parental rights
As mentioned above, parents deprived of parental rights retain the parental obligation to provide for their child, which is established by article 71 of the Family Code.
If maintenance has not been recovered prior to the deprivation of parental rights, the question of the recovery of maintenance (i.e. the amount of maintenance and the manner of payment) may be decided in the same judicial process or in a separate judicial process (i.e., by an executor or an order).
The deprivation of parental rights does not affect the amount of maintenance; they are collected on a general basis:
- 25 per cent per child;
- For two children - 33%
- Three, four and over, 50%.
Taking into account all the circumstances of the case (e.g. parents ' level of material security, lack of employment or non-permanent earnings), the court may modify the standard maintenance amounts referred to above or fix alimony in a firm monetary amount.
Adoption and maintenance
A father or mother who is deprived of his or her parental rights is obliged to pay maintenance until the child reaches the age of majority or until the child is adopted, in which case the child is to be provided for by the adoptive parent and the parent who is deprived of his or her parental rights is to be removed.
Persons interested in adoption have the right to file documents not earlier than six months after the court decision on the deprivation of parental rights has entered into force (art. 71, para.
Judicial practice
The courts of our country are seized every day of the deprivation of parental rights; unfortunately, most of them are eligible for redress, which means that every day children become orphans with live parents.
The judicial practice of depriving children of their parental rights is common, and defenceless children have to be protected from irresponsible parents; although the courts seek to maintain full families, children ' s interests require drastic and sometimes severe measures.
Example:The plaintiff, Novikova Anna Vasilievna, was married to the defendant, Novik Dmitri Andreevich, and the children were born, the daughter of Larissa Dmitriyan, son of Semen Dmitrievich.
The husband did not work, abused alcohol, physically abused his wife, put psychological pressure on his children, and the wife filed for divorce and requested maintenance from her husband.
The relationship between the former spouses has not improved since the official dissolution of the marriage.
Novikov Dmitri Andrejevic not only did not provide any assistance to Anna Vasilyevna and the children, but he also demanded money for alcohol and food, for entertainment, for debt to "friends".
The situation did not contribute to the normal development of the children, and it affected their success in school, in communicating with their peers, and in their health. No father's upbringing was possible.
Novikova Anna Vasilievna filed an action for the removal of Novikov Dmitri Andrejevic ' s parental rights against his daughter and son, after examining the evidence provided by the plaintiff, after hearing the opinion of the guardianship and guardianship authority and the prosecutor, the court granted the claims.
Legal assistance
The deprivation of parental rights is a long and not a pleasant procedure. Just imagine that you have to take away the child's right to see another parent by your own hand.
The deprivation of parental authority is often accompanied by quarrels, physical abuse, abduction of a child and other negative factors.
In addition, not all mothers know how legally to deprive irresponsible fathers of parental rights? Lack of time to go to court, a weak base, inability to resist the opposite side's attacks, and constant stress only exacerbates the case.
The best solution is to seek free online advice from the lawyers of our portal, and we are ready to provide you with up-to-date information on the deprivation of parental rights.
If necessary, you can order full legal representation, and our experts are engaged in all kinds of pre-trial and judicial work to disenfranchise parents.
With us, you can be confident that the rights of the child will be fully protected!