And if there is no dispute between the parents, the matter shall be decided by a court of law.
General aspects and objectives
- Inherited at the death of the father;
- The protection of the rights of the child is a means of meaningful communication.
Sometimes there is a need for maintenance or social assistance for the loss of the breadwinner.
Ways of resolving the issue
The legislation of the Russian Federation provides for such ways of establishing paternity:
- Free consent — when both parents do not object;
- Trials.
Automatically, a man is recognized as a father if the child is born in a registered relationship or not later than 300 days after the divorce.
Voluntary
This method is used when a man agrees with his relationship, and his right is established by a legal act (art. 48, para.
This procedure must be followed by citizens who have a common child and are not married.In order to process the documents, both of them should come to the civil registry and provide a general statement.
It is only through the courts that proof must be given if the father thinks the child is his and the mother:
- has died or has been declared incapable of exercising her rights on her own;
- Its location is unknown;
- He is deprived of parental authority.
Then the only way a citizen can take a baby home is if he's got custody.
When a child reaches the age of majority, his or her consent must be obtained before submitting an application (art. 48, para. 4).
Article 48 of the Family Code of the Russian Federation: " Determination of the child ' s origin "
Use of justice
- The alleged citizen refuses to acknowledge his or her relationship;
- The man died without documenting his paternity.
This category of cases never ends with a settlement.
Who makes the demands
The following are entitled to apply to the public services of the country for the formal establishment of paternity:
- Caregivers with a child — this happens in the event of the mother's death;
- (a) The child (at his or her own request) — when he or she is 18 years old;
- A citizen if a woman refuses to recognize him as the father of her son or daughter;
- The guardianship authorities, when the child is declared incompetent at the time of reaching the age of majority.
Read also: Exemption from maintenance
Civil courts are considering recourse.
Differences between two requirements
- Paternity — in such a case, an action is brought, both parties are heard, the dispute is heard and a decision is taken on the basis of it;
- The fact that a person has been recognized as such.
If a parent has gone away from his life, then it is only for the court to examine the evidence and make a verdict.
Documents for voluntary resolution of the question
- State act on the birth of a child or discharge from a maternity home;
- Official written communication;
- Authorization of guardianship authorities (if necessary);
- the notary ' s authorization or signature (in case of non-appearance of one of the parents);
- A certificate from a medical institution on pregnancy (if documents are submitted before the birth of the son or daughter);
- Passports confirming the citizenship of the Russian Federation;
- A check on the contribution to the budget of the Power;
- The consent of the guardianship or guardianship authorities (in the event of the child ' s incapacity);
- Written consent (when the child reaches the age of 18).
In the event that the father wishes to establish his own relationship, article 51 of FL No. 143 requires:
- The birth document of the child;
- The applicant ' s passport;
- The claim;
- The decision of the court to declare the mother of the child incompetent, missing or deprived of maternity (if necessary);
- The consent of the guardianship authorities;
- It's a check for contributions.
The official document of the determination of paternity, certified by the stamp of the registry authorities, must indicate:
- Date and place of birth of the child;
- F. I. O. before and after the procedure;
- A series and a paper number;
- Personal data of the father and mother;
- Information from the issuing authority.
Federal Act No. 143-FZ of 15 November 1997 on civil status
List of documents for the administration of justice
- A copy of the document on the State form confirming the birth of the child (required if the mother submits)
- Various evidence of paternity, joint property (including medical reports, witness statements)
- A statement of claim to which the claims are attached;
- A check confirming payment of 350 rubles.
If a maintenance case is under consideration, the woman does not have to pay the mistress.
Formation of the statement of claim
A claim may be made by:
- At the same time as the birth registration of the child;
- after some time.
In the latter case, the application must be accompanied by a document confirming the birth of the child.
Read also: Punishment for failure to pay maintenance
Such data shall be displayed in the application submitted:
- Information on the plaintiff and the defendant;
- Grounds for treatment;
- Requirements;
- List of papers filed.
There's an extra payment receipt to be provided.
Sample forms
A declaration of Form No. 12 of Government Decision No. 1274 of 31 October 1998 is required if there is a mutual desire to establish paternity.
download application form No. 12
To download a claim for paternity
Procedure for the conduct of proceedings by a public authority
- To collect the necessary evidence and make it available at court hearings;
- Collect relevant papers;
- Make a declaration (accuracy or proof of paternity);
- To pay a tax on the State budget;
- To make a decision.
The package is reviewed within five days by a judicial commission and a preliminary hearing is scheduled and the evidence provided is re-checked.
Once a satisfactory decision has been reached, the complainant applies to the civil registry for correction of the father ' s identity in the child ' s documents.
Conditions for the acquisition of legal rights by parents
- A man ' s absolute denial of his father ' s confession;
- Unregistered relations between parents;
- The consent of the guardianship and guardianship authorities.
Citizens have the right to apply to the courts before the birth of a child, for reasons such as the absence of an unregistered marriage between them, and if both spouses are unable to file a complaint after birth, and if the mother has doubts about the father ' s father ' s father ' s father ' s father ' s father ' s father ' s father ' s father ' s father ' s father ' s father ' s father, the relevant DNA tests are performed.
How to prepare and apply?
It must include such points as:
- The fact that the mother and father live together;
- Their general management of the farm;
- Listing of evidence;
- Claims for maintenance (if necessary).
Or other relationships, if any, should be specified.
There's no statute of limitations, you can file it at any time.
Evidence
The following materials may be used as evidence for the court ' s determination of paternity:
- Testimony of witnesses - written or oral (at the meeting), such citizens must confirm the fact that the parents live together and that the father is involved in the upbringing of the child;
- Laboratory blood and DNA tests — cost between 10,000 and 20,000 rubles, comparing cell structure, group, parent and child resuscitation;
- The correspondence between a man and a woman, the video footage.
There may be evidence in each particular situation, so any information that will help in the case will be better provided to the court, and there is no strict list of evidentiary facts in the proceedings.
Read also: Derogation of marriage
Recognition of a postmortem relationship
According to article 50 of the Russian Federation, when a man has left a life that is a real father, but this has not been recorded in government papers, it must be established that paternity is recognized.
- Transfer of property previously owned by the parent;
- Formalize and receive survivors ' pensions (if minor children);
- A claim for damages.
In order to do so, an action is brought before the court, and all possible evidence is provided.
Article 50 of the Family Code of the Russian Federation: " Establishment by a court of the recognition of paternity "
Data from another person
If a citizen is already registered on the State birth form, the civil registry will not accept paternity documents from the mother; this problem will have to be addressed to the judicial authorities.
If the mother does not consent
In the event that a woman does not consent to the recognition of a man by the father, a statement of claim shall be made; she shall be the defendant and the guardianship authority shall be a third party.
The parent needs to ask for an examination, and the witnesses' testimony is taken into account.
If there is strong evidence of paternity, it will not be difficult to obtain a positive result; all the paragraphs of the instruction must be carried out accurately and without errors; the length of the entire procedure is on average three months; and the legal counsel is better placed to ensure a more successful and rapid flow of the case.
List of documents for determining paternity
Family law > Parental rights > List of documents for determining paternity
The establishment of affinity between the father and the child requires a genetic examination as prescribed by law.
In order for the court to permit the procedure, the complainant must collect a package of documents, which must be submitted to the court.
We'll try to figure out what documents are needed to establish paternity to confirm a relationship with our child.
Voluntary paternity determination documents
Under article 48, paragraph 3, of the Criminal Code, paternity may be registered by joint application of the child ' s parents if the mother is not legally married.
This means that the child ' s parents must contact the registry office with a package of documents and have the paternity processed properly.
If the record was made to the ex-husband within 300 days of the divorce, it is not possible to register the child in the registry without challenging the father ' s record in court, in accordance with article 52, paragraph 1, of the Criminal Code.
If the recording was made in the register authorities by a joint declaration of paternity, but the person is not a biological father either, these persons have the right to challenge paternity through the courts.
The voluntary establishment of a relationship, depending on the situation, is subject to the mutual consent of the parents when the parents register the child with the father ' s family name.
They are expected to file an application with the civil registry.According to article 48 of the Russian Federation, there may be several options for the outcome of the case.
Parents who are not married jointly initiate the establishment of affinity.The claimants will be required to file such documents:
- Both parents ' passports;
- Statement on Form No. 12;
- The birth certificate of the child;
- If the documents are submitted before the birth of the child, a certificate will be required to record the woman ' s pregnancy;
- The child ' s consent if he or she is 18 years old;
- The consent of the guardian (if any);
- The authority or signature of one of the parents, certified by a notary, if he or she cannot be present in person;
- A receipt for the payment of the mistress.
The father without the child's mother wants to establish paternity.According to article 51 of FL No. 143, he must be provided with:
- Statement;
- Passport;
- The birth certificate of the child (if any);
- The court ' s decision to declare the child ' s mother missing, incompetent or deprived of her parental rights;
- Certificate of death of the biological mother of the child (if any);
- The court act or consent of the guardianship authorities for the recognition of paternity;
- I've got a check for the mistress's fee.
This list of documents is sufficient and may even be reduced depending on the situation and circumstances.
As a result of the birth certificate, the father will be entered into the birth certificate and a special certificate will be issued to establish the biological link of the child from the claimant.
An application can be filed if the future mother and father have reason to believe that the father may not survive the birth of the child due to serious illness.
In such a case, they may apply to the registration authorities for recognition of paternity, and medical certificates will be required to confirm the father ' s illness and mother ' s pregnancy.
Judicial documents for the determination of paternity
- It is possible to establish paternity not only on the basis of the father ' s statement, but also on the basis of the mother ' s claim.
- In the event of an application from the mother, it is appropriate to file an immediate claim for maintenance.
- They cannot be recovered from the previous period when the child was born, but can only be demanded from the moment paternity is established.
- Under article 49 of the Criminal Code, paternity may be established through a judicial authority, in the event of:
- If there is no joint application in the civil registry;
- If the marriage is not registered between the child ' s parents.
The applicant in this case may be:
- One of the parents;
- The guardian;
- The child has reached the age of 18.
The law does not establish a precise list of documents, but according to article 55 of the Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation, the following may be attached as evidence:
- Written documents;
- :: Material evidence that indicates the relationship between the child and the father;
- Testimony;
- Expert opinion.
It is essential that the evidence be obtained in accordance with the legislation in force and conform to the requirements of articles 59 and 60 of the Code of Criminal Procedure of the Russian Federation.
- Also, when a claim is filed with copies of documents, it is necessary to pay the government fee and attach a receipt.
- The court shall consider the documents submitted within five days and set the date of the preliminary hearing, which shall consider whether an expert examination is required at the request of the plaintiff or whether new evidence will be obtained.
- After the preliminary hearing, the date of the trial shall be set.
- In order to establish the truth, the parties may avail themselves of the right to choose any lawful means of proving the child ' s origin from the presumed father.
The most reliable method is the result of genetic DNA analysis, which is highly likely to confirm the relationship of humans.
But the shortcomings of this method include the high cost of the procedure, so the court can determine the relationship without this analysis on the basis of:
- Directions in the documentation where the man has positioned himself as the child ' s father or paid him alimony;
- Testimony of witnesses who can confirm the joint residence of the parents and the child.
If the other party avoids genetic analysis, the court cannot force the test to be carried out, but can prove paternity, given the refusal of the examination and other evidence in accordance with article 79, paragraph 3, of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation.
But since DNA research is only one of the evidences, it has no advantage over other facts, and the court must rely on all the facts to make a reasoned decision.
Written documents are also under consideration, such as:
- Personal correspondence, telegrams, postcards;
- Joint photos, videos;
- Notices of receipt of parcels or remittances;
- The father ' s requests for placement of the child in children ' s institutions.
- Testimony of close communication between the child ' s alleged father and his mother.
Recognition of paternity in special proceedings
- The proof of affinity is required for children who are not only born in an official marriage but also for children born out of wedlock.
- Extramarital children have equal rights with children born in a legal marriage if their paternity has been legally established in accordance with article 53 of the SC.
- If the child ' s father admitted to being his father in life but died, the mother may apply to the court to establish this fact.
- Most often, the determination of paternity is necessary for the award of a survivor ' s pension, as well as for the child ' s inheritance and inheritance.
If the deceased made a will before his death, his offspring would be entitled to a share of the inheritance in accordance with article 1149 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation and in the event that paternity is established.
The record itself is not changed by the court.On the basis of his decision, it is possible to register the birth of a child in the civil registry and to give him his father ' s surname and patronymic on a legal basis, in accordance with articles 58 and 59 of the Family Code of the Russian Federation.
Where to apply for paternity
In the court where the matter will be examined, the complainant will be obliged to confirm his identity and to provide details of the child.
Related documents shall be filed with the court in the place of residence of the plaintiff or defendantThe list of documents, together with the statement of claim, shall be transmitted through the local judicial office or the post office by registered letter.
Depending on the individual situation, the claims are based on a standard sample or on their own; the samples can be found on stands in court.
The application must be in triplicate, one for the applicant, the other for the defendant, and the third for the court.
The applicant must express his or her will in the form of a statement of claim or a written application.
It shall specify:
- The name of the court to which you file the claim;
- your data and information on the defendant: F. I. O., home and electronic address, contact number;
- Information on the child: F. I. O., date of birth, birth certificate data;
- Evidence that confirms the relationship between the father and the child;
- Application for recognition of paternity;
- A description of the case.
The following package of documents must be attached to the claim:
- The birth certificate of the child;
- Request for genetic analysis;
- Consent to DNA research;
- Statement of witnesses;
- A receipt for the payment of the monsieur's fee.
After examination of the documents and materials of the case, the judge shall ruleOnce it has been adopted by the court, it becomes enforceable.
A parent may apply to the Recording Department for registration of the document.
In order to do so, he must file an action, a court decision and a payment of a notice of the Minister of State.For 2023, it is 350 rubles..
The relevant entry will be entered on the birth certificate and the defendant will be issued with the certificate.
Similar articles:
- Contact
- Classmates
- Google+
What is needed to establish paternity: a list of court and registry documents
It was important for every child to have a full-fledged family consisting not only of a mother but also of a father; the subject of recognition of paternity could be raised entirely at any age of the minor; that was relevant even when the child was 18 years old.
The procedure may be different, so it is recommended that the documents required to establish paternity should be consulted in advance; if the father has a formal relationship, the child automatically becomes the mother ' s spouse.
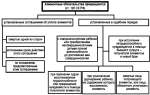
If the marriage has not taken place, there are two ways to resolve the issue: by the personal will of a person who considers himself to be a biological father, and by means of a court.
What kind of documents are you looking for?
She usually wished to receive child support from her former partner, and there were also cases in contemporary jurisprudence in which fathers themselves went to court to prove that they were related to the child.
In all circumstances, a person is required to file an application with the evidence, but the matter will be dealt with by the court; the voluntary recognition of paternity is very different from the court; in a similar situation, the application is sent not to the court but to the civil registry; and it is often a joint application.
If the mother dies or is deprived of her parental rights, then the man must come to the public institution himself, and it is recommended that the letter be supplemented by appropriate acts; after a period of time, the determination of paternity will be carried out.
List of documents for recognition of paternity in the registry
Articles 50, 51 of Act No. 143-FZ of 15 November 1997 stipulated that the establishment of paternity in the civil registry could only be done by the joint application of the mother and father of the newborn child, which was relevant in the event that the baby was born to a couple whose relationship was not officially registered.
If the mother is dead, deprived of her parental rights or missing, only one father is required to appear in the civil registry; this is also the case in cases where the child ' s mother is incompetent.
The following documents are required for the determination of paternity:
- A declaration written by the parents (parent);
- It is still important to provide applicants ' passports;
- A certificate from the maternity home is required to indicate that a living child has been born;
- In special circumstances, a court order is required to declare the mother incompetent, missing or deceased, in the latter case a certificate is sufficient.
In cases that prevent mutual treatment, the administrative registration of paternity may be carried out if the parents of the newborn have separate applications, and the recognition of paternity when applying to the civil registry may take place both at the time of registration of the child and after the issuance of the birth certificate, until the child ' s majority.
In the latter case, the adult child ' s written consent to the procedure is required; if the recognition of paternity is made in respect of a son or daughter who has reached the age of 14, the child ' s passport is required.
If the mother dies, the father has the right to apply personally to the register by attaching his passport to the application, as well as a document showing the woman ' s death; a minor ' s birth certificate is also required.
List of documents for court proceedings
The recognition of paternity through the courts shall take place in such circumstances:
- For example, if the mother has refused to include her husband ' s data in the document on the birth of a common child;
- The biological father does not recognize a child born out of wedlock;
- The father of the child is not the legal spouse of the mother; another person is considered to be the real father.
The Court should provide such documents:
Every child needs a father, and it is worth noting that it is impossible to recover maintenance without establishing paternity, and that there are no grounds for communicating with the child's family.
What evidence can be taken into account in court?
If a claim has been filed to establish paternity for a minor whose father is, on the basis of documents, another citizen, he or she shall be brought before the court to take part in the case.
This is simply due to the fact that, once the claims have been met, the information given in the certificate is cancelled; the defendant ' s agreement to recognize paternity by filing a joint application with the child ' s mother with the registry authorities for the court means that the defendant accepts the claim.
For this reason, the court is obliged to rule on the satisfaction of claims and the determination of paternity is classified as a case in which the conclusion of a settlement agreement is inadmissible.
According to article 49 of the Criminal Code, in such cases, the court is obliged to establish the only fact — the true origin of the minor ' s offspring.
It is important to note that the determination of paternity by the courts may be initiated by the Chada itself, in which case the son or daughter is required to reach the age of majority.
With the entry into force of the UK of the Russian Federation in 1996, the application of the rules of article 49 is used by the courts to hear various cases concerning the establishment of paternity of children that have been born since the first March 1996 and later that date.
In particular, the provisions of article 48 of the Code of Criminal Procedure are used, which states that in establishing paternity, such facts shall be admitted as evidence:
- If the father lives with the child ' s mother in the same dwelling area;
- The baby's supposed father and mother are in the common household;
- The father is responsible for the child ' s maintenance and upbringing after the child ' s birth, as witnessed by the testimony.
It should also be noted that the following can be attributed to the joint residence of the mother of the minor child and the defendant:
- The mother and father of the child buy common property;
- Dad and the baby's mom take care of each other.
The residence of biological parents in one dwelling area must continue until the child is born; the confirmation of one of the grounds set out in article 48 and the refusal of the child ' s alleged father to recognize himself as a father gives the court the right to order an appropriate forensic examination.
Its main purpose will be to establish the ability and inability of the defendant to conceive, which is considered to be a sufficiently serious ground for recognition of paternity.
If paternity is established for children born after 1 March 1996, the means of proof provided for in the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation shall be used:
- Parties ' explanations;
- Witnesses ' testimony;
- Third-party explanations;
- Written evidence;
- The conclusions of the expert experts;
- Physical evidence.
It is important to note that in the preparation of the paternity case or in the court ' s consideration of the case, an expert examination may be made, as appropriate, to take into account the views of the parties and the circumstances of the case requiring certain knowledge in the fields of genetics and medicine.
It is often necessary to use genetic tests that are likely to confirm or deny paternity at 99.9 per cent. DNA tests cannot be the only evidence.
It is advisable to prepare in advance that paternity cases are sufficiently complex and very long; it is recommended that family lawyers be available to protect their client ' s interests, as well as to assist in the preparation of the claim; they will provide psychological support.
—>
Documents for the determination of paternity
The establishment of affinity involves the passage of a procedure established by law.
In order to obtain a positive result, the applicant must collect a package of documents that is being executed or reviewed by the competent authority.
The article describes the specific situations and a list of documents that a citizen will need to prove his/her relationship to his/her child.
What documents are needed to establish paternity
Before going directly to the list of required documents, attention should be paid to the means of establishing affinity, since depending on the specific nature of the case and the type of legal procedure chosen, a list of the required documents is defined.
In any event, the applicant will be required to express his or her will in the form of a written application or a statement of claim; in addition, the authority authorized to examine such matters will be obliged to confirm the applicant ' s identity, to state the child ' s data (with some exceptions), and to provide additional information or evidence more similar to those set out below.
Documents for voluntary paternity determination
It is well known that voluntary action on the part of the parents (one parent) on the issue of the establishment of paternity involves the submission of a statement to the registry office, with two options available for the development of the situation, in accordance with article 48 of the Family Code of the Russian Federation.
- Parents who are not legally married together initiate the establishment of affinity.In this case, the claimants will need the following documents:
- Statement on Form No. 12 of Government Decree No. 1274 of 31 October 1998
- Both parents' passports.
- Trust or notarized signature of one of the parents if the personal presence of one of them is not ensured.
- The consent of the guardian (guardian) in the event of the establishment of a relationship with a child deemed to be incompetent.
- The child ' s consent if the father ' s origin is established for a child who has reached the age of 18.
- A certificate from a medical institution to register a woman on pregnancy, in the event of the submission of documents before the birth of the child, if there are grounds established by article 48, paragraph 3, of the Family Code of the Russian Federation.
- Birth certificate, at the same time as the birth certificate.
- The birth certificate of the child when paternity is established after the registration of the birth.
- Payment of State duty.
- Father personally, without a biological mother, wants to establish paternity in relation to his child.According to article 51 of FL No. 143, the applicant will need:
- Passport.
- Personal statement.
- Child birth certificate (if any).
- Document confirming the death of the child ' s biological mother (if any).
- The court ' s decision to declare the child ' s mother incompetent, absent or deprived of her rights to him or her.
- The consent of the guardianship authorities or the court ' s certificate of paternity.
- The tax bill(s) for payment of the duty.
In general, the list of documents submitted is exhaustive and may be reduced in the light of individual circumstances.
Judicial documents for the determination of paternity
Article 49 of the Family Code of the Russian Federation allows for the establishment of paternity through a court of law, by filing a complaint, in the event of:
- No registered marriage between the child ' s parents.
- No joint statement in the civil registry.
The plaintiffs in this case are:
- One of the parents.
- The trustee.
- The child himself, when he or she attains full legal capacity.
In this context, no precise list of documents has been established by law; however, article 55 of the Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation gives the parties the right to present as evidence:
- Written documents.
- Witness testimony.
- Material evidence, i.e. items in the material world, which directly or indirectly indicate the relationship between the father and the child (photos, videos, correspondence).
- Expert opinion, et cetera.
It is important that they comply with the requirements of articles 59 and 60 of the Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation, and that they be obtained in accordance with the rules in force; moreover, when filing a claim with attached copies of documents, they must pay a fee and submit a document confirming the performance of this obligation.
The so-called freedom of proof gives the parties the right to choose the means and means necessary to determine the child ' s origin from a particular father.
Of course, the most conclusive evidence is the positive result of the DNA test, which is most likely to confirm the relationship of two people on the basis of the genetic material submitted by them.
But the only downside of this method is the cost of the procedure, and therefore it is not mandatory at all, and in practice the court is very calm in determining the relationship without the study.
For example, on the basis of evidence of living together and maintaining a common household within a fixed period of time, according to the data given in the medical records, where the father had previously identified himself as the father of the child, the payment of alimony, etc.
Loops
Fresh records
Fresh comments
Voluntary determination of paternity
Has prepared the article.
Lawyer Denisov Ludmila
Voluntary determination of paternity
Establishment
Voluntary paternity is a procedure provided for in Russian law, the purpose of which is to determine the origin of the child in the event that the parents of the child are not married; voluntary consent implies the consent of both parents to the determination of paternity, except in the cases provided for by law.
The determination of paternity is carried out in accordance with the procedure regulated by the Family Code of the Russian Federation and the Federal Act on Civil Status Documents N 143-FZ.
The documents required for the voluntary determination of paternity, the cost of the procedure and the amount of time it takes will be discussed below.
1. When can we apply for paternity?
1.1 Before the birth of the child.
The father and mother have the right to file a joint declaration of paternity before the birth of the child, if there is reason to believe that it may be impossible or difficult to file a joint application after the birth of the child; such circumstances include, for example, the long-term mission to be undertaken; and in the absence of such circumstances, the application will be refused.
It's important to know!
If an application for paternity has been filed before the birth of the child, the registration of paternity will take place at the same time as the registration of the birth of the child, it will not be necessary to reapply; however, the application may be withdrawn by the father or mother before the birth of the child.
The withdrawal of the application will not, however, prevent the child ' s parents from applying again to the civil registry.
1.2 At the same time as birth registration
The father and mother file a joint application as well as documents for the State registration of the birth of the child.
1.3 After birth registration
You can apply for paternity on a voluntary basis after registration of a child ' s birth, at any time before the child reaches the age of majority; after the child reaches the age of majority, the child ' s consent to the procedure will be required.
2. Where and how to apply for voluntary paternity?
2.1. The application can be submitted electronically through a single municipal and public service portal (the document must be signed by a simple electronic signature of each applicant);
2.2.
An application may be submitted in writing to the civil registry authorities of the father ' s or mother ' s place of residence or the place where the child ' s birth is registered by the State (if paternity is established after the child ' s birth is registered).
3. How much will it take to pay?
The amount of the State fee charged for the State registration of paternity is now 350 roubles (this amount includes the issuance of a certificate of the prescribed model).
It's important to know!
If the application for paternity is submitted after the birth registration, the registration of the birth of the child will be amended, which in turn makes it necessary to obtain a new birth certificate; the State is responsible for obtaining a new birth certificate of 650 roubles.
4. Which documentsIs it necessary to establish paternity on a voluntary basis?
4.1 DThe registration of paternity on the basis of a joint application to the civil registry must be provided:
4.1.1. Statement on Form 12 (slip a sample with an example of filling in);
4.1.2 Parents ' passports;
4.1.3. A receipt of payment of State duty;
4.1.4. A child ' s birth certificate if paternity is established after the State registration of the child ' s birth;
4.1.5.
A marriage certificate if the child ' s parents marry after the child ' s birth;
4.1.6.
A document confirming a mother ' s pregnancy issued by a medical organization or an individual employer carrying out a medical activity if the application is submitted to the civil registry.before birthA child.
4.2 In order to register paternity on the basis of a father ' s application, which is admissible in the case of,If the child's mother is dead,The following information should be provided to the civil registry authorities, whether it is declared incompetent or deprived of parental rights, or it is not possible to establish its location:
4.2.1. Statement on Form 13 (slip a sample with an example of filling in);
4.2.2 A receipt of payment of State duty;
4.2.3.
The mother ' s death certificate, the court ' s decision to declare the mother incompetent or to deprive her of her parental rights, or the court ' s decision to recognize the mother as missing or the document issued by the internal affairs authority at the mother ' s last known place of residence, confirming that her place of residence could not be established;
4.2.4. The consent of the guardianship authorities to the determination of paternity.
6. How long has the certificate of paternity been prepared?
The registration authorities issue a certificate of paternity to citizens on the day of the application.
As you can see, the voluntary determination of paternity takes very little time and is not very difficult, but it is necessary to know the following nuances.
- If the child's father is a foreign citizen, the determination of paternity shall take place in the same manner as for Russian citizens, but a notarized translation of the passport (or other identity document) will have to be attached to the application.
- If the child's father is in detention, then his signature on the declaration of paternity must be certified by the head of the detention centre or the director of the correctional facility.
- If the father or mother does not have the opportunity to appear in person before the civil registry authorities to file an application, applications may be made by each of them; signatures to the application must be notarized.
- It should be noted that it will not be an obstacle to the determination of paternity of the disability of the father of the child, the presence of the father of the child in a registered marriage not with the mother of the child, and the minority of the father of the child at the time of the registration of paternity.
The most important thing is for the father to express his desire to go to the civil registry and to process all documents properly.
It should be understood that if a citizen knew at the time of his or her application that the biological father of the child was not his or her father but another man, he would not be able to challenge his or her paternity in the future.
- - The establishment of paternity has certain legal consequences: the father's rights to communication, upbringing and participation in his life, as well as his responsibilities, including the maintenance of the child.
- If the father or mother does not wish to establish paternity voluntarily, the party concerned has the right to file a claim for paternity with the court.
- You can order a DNA paternity check in the DNA lab with an accuracy of 99.99 per cent.
- Establish paternity by DNA
Judicial determination of paternity: procedure and procedure, recognition through court of which documents are required
The child ' s origin is established at the time of birth registration and, as a general rule, the documents are submitted by the mother; the woman presents a passport, a medical birth certificate and a marriage document; on the basis of this information, the data are included in the child ' s documents; the father ' s data are entered either from the marriage certificate or from the mother ' s words.
In the first case, a man has parental authority over a minor, and in the second, the data are included at the woman's request, without legal consequences. If the parents are not married and the man refuses to sign the child voluntarily, there will be a need for judicial recognition of paternity.
Short-term identification of the children ' s origin
Consider why paternity is to be established. In order to have parental rights and responsibilities, these men must be included in the children ' s documents. In the event of a formal marriage, the mother ' s husband is considered to be a blood parent by default and entered into the birth register; the rule also applies to children born within 300 days of divorce.
If the biological father is not married to the mother, the only option is to establish paternity.The Act provides for the possibility of including information at the will of a citizen or against his or her will; the basic condition is the requirement that one of the parents must submit the information.
If paternity is voluntarily established, the biological father must:
- To make a joint application to the competent authority;
- To submit a personal application and an order from the District Care Department to the Office of the Registrar.
A citizen pays a fee, applies and receives a certificate of paternity within one hour.
Attention!The Act provides for the possibility of addressing this issue through the IFC or the State Service ' s electronic service.
Judicial determination of paternity
The judicial determination of paternity shall apply in the following cases:
- The man does not want to recognize the child;
- The woman prevents the establishment of paternity on a voluntary basis;
- The blood father wishes to exclude the legal husband from the child ' s documents;
- The biological father died before paternity was established.
Not all men want parental rights and responsibilities with regard to blood children; the main reason for refusal is the obligation to provide for the minor; often information about the existence of a blood child is hidden from the official spouse.
The law protects the interests of the minor and the existence of an official father in the interests of the child.The matter could therefore be resolved by force.
In some cases, the woman does not wish to include the biological father in the children ' s documents, primarily because of the reluctance to publicize the identity of the child ' s blood parent, in which case the man may apply to the court.
Paternity can only be established on the application of the person concerned.
Rules for determining paternity
The change of data in children ' s documents is a complex procedure without the consent of at least one of the parents; the judicial process is a dispute between lawyers; it is not appropriate to participate in the proceedings of citizens who have no experience in such matters without a representative.
The following advice may be used to resolve the issue: judicial determination of paternity: step-by-step instruction.
Step 1: Identify the plaintiff
The procedure for the determination of paternity by the courts includes the determination of the proper plaintiff; the law limits the list of citizens who may file an application with the court; the appropriate plaintiff is recognized as:
- The biological father;
- Mother;
- 18-year-old child;
- The guardian of an incompetent parent;
- The guardian of a minor child.
Other citizens have no right of recourse to the courts on this matter; social workers and close relatives cannot initiate proceedings.
Step 2: Prepare evidence
The Act (art. 49) indicates that it is possible to provide a variety of evidence that can accurately indicate the origin of the child from the said man.
The evidence shall be admitted (Plenary Decision No. 16 of 2017):
- Medical documentation on pregnancy and childbirth;
- Parties ' explanations;
- Third-party testimony;
- Photographs;
- Video filming;
- Letters in massiers, social media, text messages;
- Bank statements with funds for the maintenance of the child from a man;
- Test results.
It matters!All evidence is equally valid, and it is not allowed to separate some kind of research from others, but in most cases, the court assigns a genetic examination that confirms or denies paternity to 99.9 per cent accuracy.
Step 3: Preparation of the claim
The determination of paternity through the court includes the preparation of a statement of claim, and the document should include the following data:
- Name and address of the judicial authority;
- Information on the proponent;
- The respondent ' s data;
- Third persons (Treasure and Registration Unit);
- Name of declaration;
- Detailed information on the grounds for determining paternity;
- Existence / absence of a de facto marital relationship;
- Availability/no close connection;
- Availability/no assistance from a man during pregnancy;
- Recognition of the child as a biological father after birth;
- Reference to the law;
- Claims, including retention of security;
- A list of the attached documentation;
- Date and signature of the proponent.
The information is summarized. There is no need to describe the situation emotionally and to include spicy descriptions.
- Errors, Marches, corrections are not allowed.
- Application for paternity and maintenanceYou can download here.
Step 4: Legal action
The documents are printed in five copies (the plaintiff, the defendant, the court, the guardianship department, the civil registry) and copies of the documents are certified by the applicant ' s signature and name.
It is possible to file an action in person or by mail. Mailing is the best option. In case of personal contact, it is possible to return the documentation for processing without sufficient justification.
The documents are sent to the court at the place where the defendant or child is registered, and the action will be taken at the place where the minor is registered only if there is a claim for material support for the child.
It matters!The law does not provide for the possibility of recovery of maintenance in the determination of paternity in the past; the reason is the lack of parental responsibilities of a man in the past.
Step 5: Trial
The recognition of paternity in court may take years, and the plaintiff therefore needs to take steps to speed up the process. The following options are possible:
- Make sure that important witnesses are brought before the courts on their own;
- It is appropriate to attach to the application a request for genetic analysis;
- Take part in the notification of the defendant of the meeting or provide details of its possible location;
- Ensure that the child is present for the study.
Step 6: Conducting an expert assessment
The determination of paternity in a court of law includes the conduct of a genetic examination, which requires a request to be made; otherwise, the judge will appoint a study on his own; for this purpose, a decision will be made on the conduct of the examination; the document shall contain the date and time of the withdrawal of the material.
Parties are required to report at the scheduled time for delivery of biological material.This is a blood test and a swab from the inside of the cheek.
The material is studied by an expert; the result of the study is an expert report; the document is not made available to the parties; the organization authorized to carry out the analysis sends the data to the court.
The law imposes an obligation to pay for the investigation on the plaintiff; if the claims are satisfied, the costs of the lawyer, the expert opinion and the public service may be recovered from the defendant.
Step 7: Judgement
If the result of the examination confirms the plaintiff ' s position, the court ' s decision to establish paternity shall be handed down; the document shall enter into force within 30 days of delivery; the defendant may challenge the decision within the specified time limit.
Step 8: Registration with the registry body
The court ' s decision was not a document confirming a man ' s paternity in respect of a child; the end of the procedure required changes to the children ' s documents; the court ' s decision and the application must be submitted to the civil registry office; the law provided for it to be submitted in person or through the IFC.
A citizen pays a fee and receives a certificate of paternity and a new birth certificate form.
Cost of establishing paternity through court
Consider the costs incurred by the person initiating the judicial paternity process in 2018:
- The claim will cost the claimant between 1,500 p.p. and 3,000 p. depending on the region.
- Legal representation in court: Depending on the legal company, the region of application, the legal experience, the amount may range from 10,000 p. to 50,000 p.p.
- The cost of the study, which includes a report for the court of 16,500 p.a.
- The value of the public service for the court is 300 p.
- If the court's decision is appealed, the amount of the Minister of State will be 150p.
- The fee for registration in the civil registry office is 1,000p.
It is difficult to determine the origin of the child against the will of the parent, which requires an impressive package of documents, an informed statement and an examination. The total cost of the process in 2018 will be at least 30,000 p.