In the first case, the list of heirs is determined by the deceased ' s will; in the absence of such a document, the law provides for a certain priority, which is the basis for the procedure of succession.
When is the sequence of legal succession used?
The priority of inheritance under the law applies in the following cases:
- There is no will;
- There is a will, but it is declared null and void;
- There is a share in the estate of the heir which he does not mention in his will;
- A citizen has the right to a compulsory share, which is also not provided for in the will;
- Recognition of the heir as unworthy;
- The heir of the will gave up his inheritance.
In the light of the reasons given, inheritance may be registered under the law, both in the absence of a will and in the presence of a will; this makes the question of the order and order of succession relevant.
The duration of the inheritance for all releases is one and six months.
The sequence of succession
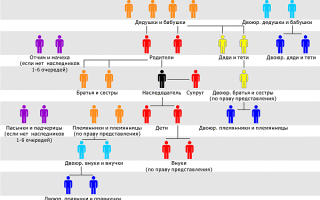
Succession under the law involves seven lines formed on the basis of family and marital ties.sequence:
- In the absence of a will, the property will inherit first line;
- If there are no recipients in the first round, the notary is looking for the heirs of the second circle;
- In the absence of a second-line heir, a third circle and so on is identified;
- If no heir is found in the deceased, the property is transferred to the State.
In one circle, the heirs haveequal rightsFor example, if six beneficiaries of the first-line inheritance are identified, the property is divided into six equal parts.
Who inherits first?
The inheritors of the first line shall be:
- Children of the inheritor;
- :: A spouse who has a public registration of a marriage;
- Parents, if they have not been deprived of their parental rights.
The children of the deceased are given equal treatment, born in marriage, out of wedlock, and adopted, all of whom are entitled to their share of the inheritance; this is also the case if the heir has been deprived of his parental rights.
Heirs to Release 2
The inheritors of the second line are:
- Affiliated and half-brothers;
- Grandparents for each parent.
In the former case, it is also understood that all brothers and sisters are equal, and it is sufficient to have a single parent in order to have a relationship and an appropriate inheritance.
The grandparents inherit on equal terms with their brothers and sisters; if the heir has been adopted, the parents of the adopter are also entitled to receive the property.
Releases 3 et seq.
In the absence of first- and second-line persons, the right to inherit shall be transferred according to the following priority:
- Release three — aunts and uncles, cousins;
- The fourth is great-grandfathers and great-grandmothers;
- The fifth is cousins of the heir, as well as cousins and grandparents;
- The sixth is great-grandparents, cousins and aunts;
- The seventh line gives the right to inheritance to relatives without blood ties — stepmother and stepfather, stepdaughter, stepdaughter.
Heirs to the submission
The right of representation is the possibility of the right to inherit from the parents, a situation that arises when the heir dies sooner or at the same time as the heir, in which case the children of the heir receive the property.
The right of submission also takes into account priority and is intended only for the first three categories of persons.
- The grandchildren of the deceased — in the event of the premature death of the children, they become the heirs of the first line;
- nieces or nieces inherit in the line of kin and full brothers and sisters.
- cousins inherit instead of aunt or uncle.
It is emphasized that only the property to which the deceased heir is entitled shall be inherited by virtue of the right of submission; if he is found to be unworthy, the right of submission shall not apply.
Mandatory heirs
Mandatory heirs are the incapable dependants of the deceased, who receive a share of the property irrespective of priority and the existence of a will.
- The children of the deceased who have not attained the age of majority;
- Persons with disabilities and pensioners who are dependent on the heir at the time of his death.
Mandatory heirs may not be deprived of their right to receive property, and their share of the inheritance is not less than half of the property.
Inheritors of Phase I
When the issue arises of obtaining the property of a deceased citizen, in most situations he or she will inherit the first line of succession, only if he or she is absent, and in the case of a written will, will it be possible to transfer the inheritance rights to other persons.
The law clearly defines the list of first-line heirs who have an advantage over other relatives, close persons and the State, and regulates the right to inherit first-line succession in article 1142 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation.
Who are the inheritors of the first line
This line of legislation includes spouses, parents and children, although it is easy to identify the heirs in this case, there are a few nuances that need to be taken into account in such a situation, since there are widespread misconceptions about this.
- A spouse may only be regarded as the heir of the first line of marriage if he or she has a legally registered marriage. The concept of "civil marriage" or "cohabitation" in common is not provided for by law. Thus, an informal spouse may be considered to be the he or she solely by will or if he or she has been legally dependent on the deceased for a year, but is not able to work, either for reasons of health or age. An age disability occurs from the age of 60 to the age of men and from the age of fifty-five to the age of women.
- The parents of the deceased have equal rights in respect of their children, including in cases where the marriage has been dissolved.
Children must be of certified origin in the order of the UK of the Russian Federation in order to obtain their inheritance.
At the same time, they are obliged to have the right to inherit property – that is, not to be legally recognized as unworthy heirs; children who are not able to work are not part of the first line of succession.
Children born to the deceased within 300 days of the discovery of the inheritance are also assigned to the heirs of the first line.
When they have the right to inherit
If a will has been made and certified notarized, the current procedure of succession is completely ignored in favour of the persons named in the will.
However, if, upon the death of the heir, he has property or intellectual rights over property not specified in the will, the property is distributed on general grounds, unless any of the heirs of Release 1 have been identified in the will as knowingly deprived of the heir ' s inheritance by the will of the heir.
Who can inherit on an equal footing with the first
In addition to the immediate heirs of the first line, there is the right to be represented by the inheritance; it is only for the direct descendants of the children of the heir if, at the time of his death and the discovery of the heir's inheritance, the heir's children are not alive; and the share of the children is equally distributed among their children, the grandchildren of the heir.
And if there are no grandchildren, then by the right of submission, the inheritance shall be passed to the next descendants, the great-grandsons or the great-grandparents; and in the other line of succession, the right of submission shall not apply – thus, the children of adopted children shall have no right of inheritance in general, except in cases of dependency.
In addition, the law provides for the concept of a compulsory share, which applies to dependent persons who are unable to work for a period exceeding one year prior to the opening of the inheritance, and is intended to ensure that persons who are dependent on the heir, regardless of their inheritance or even the immediate will of the deceased, are entitled to it.
The compulsory share applies even if there is a will in which the person entitled to it is not identified as the heir, or if his share under the will is lower than the half of the share due to the legal heirs in the application of the inheritance law on general grounds.
A person may be deprived of his or her compulsory share only by a court decision if he or she is found to be unworthy.
How shares are distributed among first-line heirs
The first-line heirs have exclusively equal rights before each other, except for those who inherit by right of submission – their total share corresponds to the share that would have been given to their parent.
However, the law provides for the right to refuse the inheritance – in the event that all members of the first line refuse – the right to inherit is passed to the heirs of the second line and thereafter.
Can the heir of the first line be left without inheritance?
In the event that the testator has made a will, the standard principles of inheritance law are not applied; thus, the heir may transfer all his property rights to any person, including a non-inheritor.
- In addition, the will also provides for the establishment of certain conditions for the inheritance – in the event of non-compliance, the person named in the will may simply not be entitled to the inheritance, or be deemed to be an unworthy heir if the conditions implied that they would be fulfilled after the inheritance.
In addition, both the existence of a will and the resolution of inheritance issues on general grounds may render the heir unworthy.
The decision that the heir is not worthy shall be taken solely by the court in cases where the person committed intentional acts aimed at obtaining the inheritance, consisting of both criminal offences or administrative offences and acts not subject to punishment but contrary to morality.
For example, an unworthy heir may be deemed to be one who has not notified the other heirs of the death of the heir with a view to entering into inheritance independently after the expiry of the period allowed to inherit.
However, if there is professional legal assistance, the will may be challenged by the courts, as well as the distribution of inherited shares in the application of common grounds; most of these legal disputes are primarily won by highly qualified lawyers.
Priority for inheritance
If there is a will, the order of succession is only relevant to the law; if there is a will, the order is irrelevant; there is only a compulsory share of the inheritance for minors or disabled children, spouse and parents (subject to additional conditions and other dependants).
To what end the order of succession is determined
In accordance with the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, the heirs inherit in accordance with the established order of succession, which means that the heirs of one line of succession have the right to receive the inheritance in equal shares after the opening of the inheritance.
The heirs of each succession, after the first line, will be entitled to inherit only in the absence of the heirs of the previous line.
Either where such heirs are deprived of their inheritance, have no right to inherit, are excluded from the inheritance, have renounced it or have not accepted it within the statutory time limit.
There are situations where the heir of the law dies at the same time as the heir (e.g. the wife died in a car accident) or before the opening of the inheritance, so the heir of the law of the first, second, or third, died before the death of the heir or at the same time as the heir.
And if the parents were to be called to the inheritance, they would surely be of those who are dead.
If they are alive but have abandoned the inheritance, there is no right of submission and the next line of succession is called for.
The heir of the deceased shall have only that which his deceased parent would have received; and if there be more than one heir, then the share of the deceased shall be equally divided between them.
Who inherits first
The children, the spouses and the parents of the inheritor are the first to be asked to inherit.
At the time of the marriage, the share of the spouses in the common property is first allocated to the common property and then the estate is determined (e.g., the common property apartment is bought during the marriage, so that 1.2 shares are owned by the spouse according to the rules of the common property regime, and the remaining 1.2 is divided equally between the surviving spouse and the children).
No unworthy heirs will inherit, i.e. those who have committed unlawful intentional acts against the heir or his heirs (the fact must be established by a court judgement that has entered into force).
The parents shall not inherit after their children if they have been deprived of their parental rights and have not been restored on the day of the opening of the inheritance.
These rules apply to the heirs of any line of law.
And when there is no heirs of the first line, or of the first line, or of the first line, or of the first line, or of the first line, or of the first line, or of the first line, or of the first line, or of the first line, or of the first line, or of the first line, or of the first line, or of the first line, or of the first line, or of the first line, or of the first line, or of the first line, or of the first line, or of the first line, or of the first line, or of the first line, or of the first line, or of the first line, or of the first line, or of the first line, or of the first line, or of the first line, or of the first line, or of the first line, or of the first line, or of the first line, or of the first line, or of the second line, or of the second line, or of the second line, or of the second line, or of the second step, or of the second step, or of the second step.
The third is the uncles and aunts of the heir, including those who are full of respect for the heir ' s parents and incomplete.
- The fourth generation is relatives of the third degree: great-grandfathers and great-grandmothers of the heir.
- The fifth generation is the children of the nephews and nephews of the heir (the two grandchildren and granddaughters) and the siblings of his grandparents (the two grandparents);
- Release six is the children of the cousins and granddaughters of the heir (the great-grandparents and great-granddaughters), the children of his cousins (the twin nephews and nieces) and the children of his cousins and grandparents (the twin uncles and aunts).
- In accordance with the law, stepdaughters, stepdaughters, stepfathers and stepmothers are called as heirs to Release 7.
Exceptions to succession
In addition to the cases expressly provided for in the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation, which deny the possibility to inherit (unworthy heirs, etc.) as mentioned above, certain categories of citizens may claim part of the inheritance, and we refer to cases established under article 1148 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation.
- These are relatives who are unable to work on the day of the discovery of the inheritance of any degree of relationship and who are dependent on the heir for at least one year before his death; the fact that they live together is irrelevant.
- All other citizens who were not relatives but lived with the heir and were dependent on him for at least one year until the day of his death.
If there are no other relatives, they will be the heirs of the eighth, and if there are no other relatives, they will be the heirs of the eighth, and if there are no relatives, they will be the heirs of the eighth.
This is the order of succession established by the SC of the Russian Federation, which must be taken into account by the heirs when accepting the inheritance.
Destination of succession
According to 2017 statistics, in Russia, citizens turn to a notary to make a will in58-70 yearsMany citizens do not care about the distribution of their property after death.42%In cases of inheritance under the law, it is only through judicial proceedings.
It is important to understand that the article describes the most basic situations and does not take into account a number of technical points.
Call and solve your questions right now -- it's quick and free!
This can be avoided by familiarizing itself with the legal basis of the asset transfer process.
Conditions of inheritance under the law
In Russia, property may be inherited by legal entities, individuals or the State.
It is always possible for a citizen to identify persons who will then dispose of the inheritance by leaving a will; the document is subject to change at the discretion of the testator; but if the natural person has not expressed the will of the notary in advance, the law provides for the transfer of the property to the relatives.
Chapter 63, arts. 1142-1145 of the Russian Civil CodeIt is stated that the inheritance may be inherited by the relatives of eight consecutive members.
The inheritance shall be distributed equally between relatives of the same degree of kinship or in full to one heir when he is the only member of the line.
Priority of inheritance
Part III of the SC of the Russian Federation introduced significant changes in the order of succession in 2002, which is still relevant today. The potential range of heirs has increased.from 2 to 8 ReleasesAffiliation.
This makes it clear that it is not possible to transfer the inheritance to the hands of the State because of the absence of close relatives, since any single distant relative, even an incompetent, can inherit (the eighth circle of relatives includes dependants, persons with disabilities who have been under the guardianship of the last year from the date of the heir ' s death).
The degree of kinship determines the number of births between related persons, starting with the next person born after the heir.
The right to inherit is transferred in another order if all members of the previous line:
- Have not indicated a wish or action for the conversion of property;
- Overdue re-formation period(more than 6 months)..................................................................................................................................;
- Exempted from obtaining it by law;
- Dead;
- Deposed of inheritance by will of the heir.
It's possible to get a legacy fromright of submissionThe next of kin of the heir.
Right of submission
Many of the circumstances of the sudden death of the heir, without the fact that the inheritance has been converted into his own name, are passed on to his heirs (art. 1146). These are people of the nearest kind, so that they may inherit equal parts not only of the inheritance from a relative, but also of the material goods which he had not previously acquired under the law.
There are situations where a relative cannot inherit:
- And when he had made a bequest, he said: "O my Lord!
- If the heir is dead and unworthy of the inheritance of values, his relatives will not be able to exercise the right of representation.
Participants in Release 1
Who comes first of all to the heirs?
- Children (sons or daughters regardless of seniority);
- Father and mother;
- husband or wife.
If the first-ranking family did not exist or died earlier, or at the same time with the heir, they did not claim to inherit, the grandchildren or their followers may inherit the property under the right of submission.
An exception is the potential heirs without the possibility of obtaining an inheritance share of the property.art. 1146 of the Russian Criminal Code).
In order to confirm the relationship with the heir, documents must be provided. For priority relatives, this may be:
- The original and the copies of the passport;
- Birth certificate, marriage certificate.
If you are in a distant relationship with the heir, you will have to provide several documents that are related and clearly related to him.
What is the distribution of the inheritance among the inheritors of the first line?Equal parts between all members of the same line of relationship, or in full, are handed over to the sole heir in cases where the heirs of the same group are no longer present.
Second circle of relatives
The second round consists of:
- Grandparents on the mother and father lines;
- Bloody and half-brothers.
The right to inherit arises in the second line in cases of:
- Refusal or voluntary rejection of values by all members of Release 1.
- Deaths at the same time with the heir or prior to the discovery of the inheritance (by right of submission).
The children of full and incomplete brothers and sisters can obtain property according to the right of submission.
To confirm the relationship of the second line, please provide the notary with documents: birth certificates, marriage certificates, and passports.
The inheritance is distributed in equal shares.
Participants in Release 3
The brothers and sisters of the heirs' parents occupyThe third line of kinshipThey will inherit if the family of the previous group does not exist or they have abandoned property.
The right of representation enables cousins and cousins to inherit material assets.
In order to obtain inheritance benefits, documents are required that identify the relationship with the potential heir, ranging from passport to family composition certificates, to statements from the civil registry.
The property is divided equally among the heirs who take over the right of disposal.
Heirs of successive rounds
Up to 5 - 8 groupsThe succession is rarely obtained, but the SC of the Russian Federation describes such situations and treats the following relatives as such persons who may inherit material goods:
- First parents to the fourth line;
- Grandparents, grandparents, grandchildren in line five;
- Uncles, aunts, nephews in line six;
- Stepmothers, stepfathers, stepparents and stepdaughters by the seventh;
- Disabled natural persons by the eighth.
Legacy of succession by law5 - 8 groupsis similar to the conditions of previous priorities, as is the process of establishing affinity based on the number of births in the generation.
To establish a relationship with the natural person, the heirsReleases 5 - 8For example, passports, birth certificates, marriages, adoptions and hospital health certificates are also needed.
Since it is more difficult to establish a distant relationship, we should discuss in advance with the notary what documents are needed.
The heirs of one degree of priority receive the same property.
Conclusion
Legacy of inheritanceplayed a key role in the distribution of property when the citizen failed to express his or her will in the form of a document.
Current inheritance legislation is structured as follows:
- Any natural or legal person, the State, may inherit material property if the inheritance occurs in accordance with the law and not through a will.
- The likelihood of a transfer to the State is almost zero, as the relative priority has been increasedUp to 8 stepsa relative of any degree of kinship will be able to obtain the estate of the heir if the previous heir has not made himself available or for any objective reason other than the situations envisaged.art. 1146 of the Russian Criminal Code.
- The conditions and procedure for the establishment, distribution and accession of heirs are the same for all participants in the 8 rounds of kinship.
- The most important and binding condition is documentary confirmation of the relationship with the heir; it is not impossible to collect several documents from which a fully-fledged related tree will be seen.
- The right of submission enables the blood relatives of a potential heir to obtain property if he dies before the right of the owner has been acquired.
- The SC of the Russian Federation guarantees the integrity and security of the material goods transferred by excluding the transfer of inheritance to persons, which prevented the secret and independent expression of will (art.art. 1117).
- The heir may sue if he or she has a claim in the inheritance-sharing process or considers that his or her rights have been infringed.
Inheritors of Phase I
The first heirs who are entitled to claim the property left behind by the heir are the heirs.Relatives of the nearest circle:: Children of all ages, spouses (if alive) and parents of the deceased, as stipulated in article 1142 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation and referred to as the first line of succession.
The list of priority heirs may changeThis is due to the refusal of any of the successors to inherit, to declare them unworthy, or to become a dependent.
In the event of the death of one of the adult children of the heir before the opening of the inheritance, it is assumed that his descendants (the grandchildren of the heir) will inherit instead of the deceased.
Priority heirs are deprived of their rights if they are recognized by a court of law.UnworthyAs a result of the injury to the heir or the lack of care for him during his life, as well as the interference of other heirs in obtaining their share (art. 1117 of the Code of Criminal Procedure).
The heir also has the right to deny any of them the opportunity to inherit without explaining the reasons (article 1119 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation);with the exception of the right to a compulsory share.
Inheritor ' s spouse
The first line of succession includes the surviving legal spouse of the heir.not applicable to ex-husband and wifeAfter the termination of previous marriages, as well as of the civil (unregistered) spouse.
The latter claim is not one that permanently deprives the said persons of part of the estate of the heir, but the former spouses may try to prove their contribution to the improvement and development of the deceased ' s property made by them after the divorce.In court.
If the disabled civil spouse has lived with the heir for more than a year and has received basic means of subsistence from him (i.e. dependent), he or she will be able to inherit on an equal basis with the children and parents of the deceased husband/wife (art. 1,148 (2) of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation).
In addition to the inheritance share, the spouses are often co-owners of the estate of the heir, such as the co-owner ' s apartment.priority right to an object of inheritance(art. 1168).
Even if the legitimate spouse is physicallydid not liveWith the heir before his death, he will still be considered the successor to Phase One.
The parents of the inheritor
The ability of parents to inherit their childrennot limitedAge, legal capacity, blood relations between them.deprivation of parental rightsin relation to a particular child, and not always.
- However, article 1147 of the Criminal Code states that:Adoption is tantamount to a blood relationship..
- Parents may not inherit a child if they are deprived of their parental rights in respect of him or have been adopted by other persons (art. 1147, para. 2, of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation).The blood relationship is interrupted.The exception is where a court has granted parents the right to communicate with children by descent.
Children of the inheritor
The law provides that inheritance may be claimedAll children of the heirirrespective of their age and legal capacity, whether born in or outside a legal marriage, the total number of children of the parent or the number of his or her marriages.
Foster children will inherit on an equal basis with their relativesThe stepdaughter or stepdaughter, if not formally adopted or adopted by the heir, only belongs to the seventh line of succession.
The adopted child inherits only the adopted parent, but not the adopted parent (art. 1147 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation).
A son or daughter born out of wedlock hasequal rightswith the other children of the heir if the child is identified as a parent on the birth certificate.
Otherwise, you're gonna have to be a parent.prove in courtWith the assistance of witnesses, forensics and other methods.
Within the framework of the interests of the State party ' s State party ' s State party ' s State party ' s submission to the Committee on the Elimination of Discrimination against Women, the Committee notes that the State party ' s submission to the Committee on the Elimination of Discrimination against Women on the basis of its submission to the Committee on the Rights of the Child on the basis of a report submitted by the Committee on the Elimination of Discrimination against Women on its third periodic report was due to the State party ' s submission to the Committee on the Elimination of Discrimination against Women on the basis of the Committee ' s consideration of the Committee ' s concluding observations.Unborn childrenThe law recognizes the right to inherit the deceased parent after his or her birth (art. 1166). If such a child is present, the issuance of a certificate of right to inherit is postponed until his or her birth.
A minor child has the right to inherit property that can only be used in the future.GuardiansThey need to be authorized to carry out any transactions with property.
If the children were born in a marriage that was subsequently declared null and void, they have the right to inherit the same rights as those of other descendants.
Heirs to the right of submission
The right of submission implies that in lieu of the deceased successorAnd he shall be called to the inheritance of his offspring.Among the heirs of the right of submission are the grandchildren of the testator who are the children of the deceased son or daughter (art. 1142, para. 2, of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation).
Only the descendants of a dead adult child may inherit.independentlyTheir sons and daughters are not involved in the process, i.e. all children of the inheritor are invited to inherit property, but not necessarily all grandchildren.
This rule of lawimplies a fair division of propertyleft by a dead man, between all the branches of the next of kin.
The succession will not occur if the deceased heir has been deprived of the right to claim his share of the inheritance, which may have been facilitated by the decision of the heir or the court.
Access to a mandatory sharenot transferred by right of submissionIt may be claimed by children, parents or the heirs ' spouse, but not by their grandchildren.
Successors are not able to claim priority to use or receive an indivisible item.
Example
L. applied to the court for an extension of the period of succession after his grandmother, for whom L. was the heir of the right of submission. The girl lived in the house of the eldest relative and claimed him, but did not have time to appeal to the notary within the prescribed six-month period. The court granted the plaintiff ' s claim, without taking into account the fact that L. could not be the heir to the right of submission. Her mother, i.e. her grandmother ' s daughter, was alive at the time of the opening of the inheritance and even testified at the court hearing. Following an appeal to arbitration, the court ' s decision was quashed as not in conformity with the law because all the special features of the case had not been taken into account.
is requested to apply to the court on its own in order to restore the duration of the inheritance.
Unable to work dependants
In addition to the heirs of the first line, they are called upon to inherit.DependantsThe rule of law provides that the interests of dependent persons, who need not be relatives of the deceased, shall be taken into account.
In order to obtain inheritance in the first place, it is sufficient for a relative to receive monetary or other assistance from the heir.1 yearThis assistance should form the main part of the dependent ' s budget.
A person who is unable to work and who is materially dependent on the heir may inherit from him or her in the first line,Not even as a relative..
In order to do so, it must not only be dependent but must also live with the citizen who left the inheritance at least one year before its death (art. 1,148 (2) of the Russian Civil Code).
DependentCould be the only heir.having no consanguinity with the heir if the latter does not have any blood or foster relatives (art. 1,148 (3) of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation).
Conclusion
- The law assigns to the heirs of the first line all the children of the heir, his spouse from marriage, legal to the day of the opening of the inheritance, and living parents.
- Right to enter the first circle of inheritanceindependent of the age and mental state of the successor.
- If one of the children of the inheritor is not alive at the time of the discovery of the inheritance, the heirs ' grandchildren are entitled to his or her share of the inheritance.
- To the first circle of heirs can be assignedDependentwhich was in the custody of the deceased.
Question
The succession is claimed by three first-line successors, one of whom applied to the notary for the commencement of the inheritance, the other two (my own brothers) living in another province, the notary refused me, and he was motivated by the refusal of the application from all three heirs at the same time.
Can he demand that?
He is obliged to accept your application and to notify the other heirs himself that they can also express their will, so he will ask their addresses from you. If he does not accept the application, write a complaint against him to a notary office.
Question
I applied for my father's (home) inheritance, and while I was collecting the documents, it turns out that his mother (my grandmother) made the same application six years ago, and it's not known if my grandmother is alive now, and the notary believes that even if she is no longer alive, the house will have to be split in half, and the other half will have her sister instead of her grandmother.
Could that be the answer?
Your grandmother has the same right to inherit as you, as the successor of the first line. If she dies, her children or her spouse will have a portion of her, but not her sister. The exception is that if a woman leaves a will, she can identify anyone as her heir.
You'd better talk to your grandmother for once in so many years, find out her intentions, and at least get a lawyer to help you.
Question
My grandmother gave my father a house, he gave him a gift, he got his property, he recently died, who's going to be his heir after him? My mother died, he has no other children.
In this case, you and Grandma will be the inheritors of the first line.
Priority of legal succession 2023
All sequences of heirs under the law What line of succession for grandchildren How will the incapable dependants inherit
The inheritance is most common in our country and is carried out in accordance with the strict order of priority established by law.
There are the following:principles of inheritanceby law:
- The inheritance is based on affinity and a marital relationship with the heir.
- The list of persons who are legally inheritors is strictly defined by law and is exhaustive.
- The inheritance is divided only between the heirs of one line of succession and in equal shares.
- The right to inherit shall be passed from one line of succession to the next only in the absence of the heirs of the previous line, and in the absence of the heirs of the first line, the heirs of the second line shall be called, and so on.
All successions by law
Civil law provides forin.............................................................................oOhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhSeven rounds of succession:
- First, parents, children, spouses of the inheritor, including adopted children and adopted parents
- Second line - full and half-brothers/sisters/grandparents/inheritor ' s grandparents
- Release three - aunts/uncles of the heir
- The fourth is the great-grandfathers and great-grandmothers of the heir.
- Release 5 - cousins/granddaughters (children of nephews) and cousins/grandparents of the heir
- Release six - great-grandparents/granddaughters, cousins/uncles, cousins/inheritor's niece
- Release seven - stepparents/daughters, stepfather/mother of the heir
- Release 8 - Unable to work dependants of the heir who are not related to him (only if there are no heirs to all previous steps, will they inherit on their own in the order of Release 8. See below for further details)
What a line of inheritance for grandkids.
A lot of people are wondering,to which line of succession the grandchildren belongwhether they can inherit from their grandparents with their living parents, what to do to their grandchild if the heir's son doesn't accept the inheritance.
In the first three stages of succession, the legislator included grandchildren and their descendants (1st line), nephews and nieces (2nd line) and cousins and heirs (3rd line), but with one reservation –These persons may inheritheir's propertyRight of submission onlyYour parents.
In accordance with article 1146 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, succession by right of submission is possible only if the direct heir has died before or on the same day as the heir, in which case the portion of the heir's inheritance shall pass to his children or grandchildren, i.e. they shall inherit in his place.
Consequently,in a living parent grandson Cannot claim inheritanceThe right to inherit in this case belongs entirely to the direct heir of the first line, and even the fact that the direct heir will not accept the inheritance after the death of the heir does not give his children the right to claim the estate of the heir.
In this way, it can be distinguished.Basic rules of succession under the right of submission:
- This type of inheritance is provided forin the first three rounds onlySuccession
- Succession by right of submission is possible onlyon condition of the death of the heirbefore the death of the heir or at the same time (one day) with him
- A grandson can't inherit.after grandma/grandfather, if his parent is alive, i.e. the direct heir according to law (the same applies to nephews/nieces and cousins/inheritor ' s cousins)
- If the heir gives up his inheritance, or if the heir does not inherit it,his children do not have the right to inheritInheritor ' s property
- HeirCan't say no.from his share of the inheritancein favour of their children
- Proportion of inheritance passed by right of submissionEquivalentbetween the heirs of the right of submission
- Children of an unworthy heirand the heir,Uninheritedcannot inherit by right of submission
How the Incapable Dependants of the Inheritor will inherit
Because the questions are:What is the fate of those who are unable to work?, How will the dependants inherit according to the law,The procedure for inheritance by such persons should be explained in more detail.
The incapable dependants of the heir are classified as a separate category of legal heirs, so let's start by figuring out who the incapable dependants of the heir are.
First of all, we need to understand what's going on.The categories of persons unable to work are:
- Minors
- Citizens who have reached retirement age
- Persons with disabilities in group I, II or III
Second, legally relevant fact--Dependency of the heiris assumed to have received at least one yearTotal Contentsfrom the deceased, or systematic assistance, and that assistance was his.Main sourceThe Government of the Republic of Moldova is committed to the promotion and protection of human rights and fundamental freedoms, as well as to the promotion and protection of human rights and fundamental freedoms, as well as to the promotion and protection of human rights and fundamental freedoms, as well as to the promotion and protection of human rights and fundamental freedoms, as well as to the promotion and protection of human rights and fundamental freedoms, as well as to the promotion and protection of human rights and fundamental freedoms, as well as to the promotion and protection of human rights and fundamental freedoms.
According to article 1148 of the Criminal Code of the Russian FederationUnable to work dependants of the heir in succession have An advantage over other heirsthat is, they are entitled to inherit together with the heirs of the line which is called upon to inherit, and to inherit from them in equal shares, even if they do not enter into the appropriate line of succession.
These heirs can be divided into two groups:
HThe dependents of the inheritor who are able to work,Affiliated with himand his legal heirs, but not members of the group of heirs, which are called upon to inherit, may exercise the priority right to inherit under the following conditions::
- At the time of the discovery of the inheritance (inherior ' s death), they were unable to work
- At least one year prior to the opening date of the inheritance (the heir ' s death) were dependent on the heir, irrespective of whether or not they lived with him.
Unable to work dependants of the heir,Not relatedAnd with the heir, and therefore not in any of the seven stages of his heirs by law; these persons shall inherit on an equal footing with those who are called upon to inherit, under the following conditions::
- At the time of the discovery of the inheritance (inherior ' s death), they were unable to work
- At least one year before the opening date of the inheritance (inheritor ' s death) were dependent on the heir
- Lived with the heir.
Take an example:If the incapacitating dependent of the heir is the heir of the third line, but there are heirs of the first line, who are called upon by law to inherit, the incapacitating heir is entitled to inherit together with and on an equal basis with the heir of the first line.
If the incapacitation of the heir is among the heirs of the line that is called upon to inherit, he shall inherit together with all of them.Joint Meeting of the RID Committee of Experts and the Working Party on the Transport of Dangerous Goodshowever, the mere fact that he is an unfit dependent of the heir does not increase his share of the inheritance, i.e. the shares of all heirs are considered to be equal.
IfThe heir has no heir.All seven rounds, then his incapable dependants, who are not related to him,And those who are not his heirs by lawwill inheritOn its own,It's okay.Release 8inheritance.
This is the procedure of succession by the incapacitating dependants of the heir.
In practice, however, it is not easy to realize the priority right of inheritance.
The fact is that if the heirs challenge the fact that a person is dependent on the heir and do not agree that he or she has the right to inherit on an equal basis with them, the incapable dependant will have to prove that the he or she is dependent on him or her in court, since this fact is a prerequisite for priority inheritance under the law.
In the event of such difficulties, it is imperative thatCall on an experienced genetic lawyer,Since the inheritance proceedings of a disabled dependant presented certain difficulties, it required clear evidence on the part of the plaintiff, and legal knowledge and experience was indispensable.